Video • Organ restoration
First successful regeneration of diseased kidney
In a world first, scientists from Singapore and Germany have shown that regenerative therapy to restore impaired kidney function may soon be a possibility.

In a world first, scientists from Singapore and Germany have shown that regenerative therapy to restore impaired kidney function may soon be a possibility.
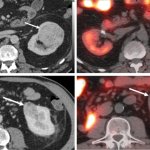
99mTc-Sestamibi SPECT/CT can aid in the diagnosis of solid renal lesions, especially in cases where contrast enhanced CT findings are inconclusive, according to researchers from the Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, Missouri.

Renal cell carcinoma is among the fifteen most common cancers worldwide. Dr Titus Brinker, from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), looked at whether a convolutional neural network (CNN) can extract relevant image features from a typical H&E-stained slide to predict 5-year overall survival.
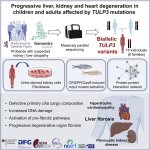
Scientists have identified a new disease in a ground-breaking discovery that could help patients with unexplained liver and kidney problems.

Rising temperatures due to climate change will lead to an increase in cases of kidney stones over the next seven decades, even if measures are put in place to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
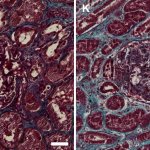
The Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infects the kidneys and contributes to tissue scarring, as shown by researchers from Germany and the Netherlands.

Digital technology solutions create new opportunities in diagnosis and assessment of renal conditions. With whole slide imaging (WSI), improved workflow and better visualization, such technology already yields a ROI for hospitals and laboratories.
Researchers have leveraged the power of digital pathology and computational modeling to detect and quantify podocytes, a specialized type of cell in the kidney that undergoes damaging changes during early-stage kidney disease.
The first investigational transplantation of a genetically engineered, nonhuman kidney to a human body was recently completed at NYU Langone Health—marking a major step forward in potentially utilizing an alternative supply of organs for people facing life-threatening disease.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disease in western countries, with an increasing incidence worldwide. Consequences of NAFLD can also include kidney disease and kidney stones, although the mechanisms for the development of these kidney complications as a result of NAFLD have not yet been fully explained. Researchers at the Leibniz Research Centre for Working…
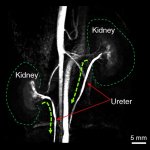
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is widely used to identify the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels. Contrast agents improve the visibility of the structures and offer more accurate information of vascular conditions such as vascular blockage and stenosis. Commonly used gadolinium-based contrast agents must be administered in chelated forms due to the gadolinium ions' high toxicity and pose…

Hemodialysis patients routinely experience side effects such as fatigue, lightheadedness and nausea during their treatment sessions. But patients in a study who used a virtual reality program to engage in a mindfulness/meditation exercise reported that these treatment-related symptoms were greatly reduced. Patients in the study wore a head-mounted virtual reality display to participate in a…
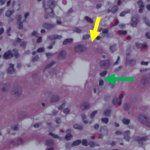
An autoimmune side effect of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) drugs could signal improved control of kidney cancer, according to a new study by researchers in UT Southwestern's Kidney Cancer Program (KCP).
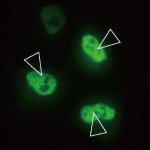
Human cells need to work like well-oiled machines to keep our bodies running as they should. Waste products such as misfolded proteins, damaged cellular components, and carbohydrates get in the way and must be quickly disposed of. Dealing with this cellular “trash” are spherical, membrane-bound organelles called lysosomes filled with a mixture of potent enzymes. In a process called autophagy,…
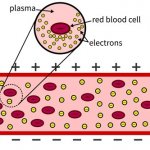
Scientists at the University of Delaware and Princeton University have developed a method to monitor blood damage in real-time. “Our goal was to find a method that could detect red blood cell damage without the need for lab sample testing,” said Tyler Van Buren, an assistant professor of mechanical engineering with expertise in fluid dynamics. The researchers recently reported their technique…
A course of action to early detect and treat severe courses of COVID-19 infections has been developed by an expert-team of the University Medical Center Goettingen (UMG). A simple urine test is intended to help medical professionals to recognize warning signs of future decompensation of COVID-19 infections earlier. With the help of a few parameters, the treatment of imminent complications can…

St Helier Hospital in the London Borough of Sutton – part of the Epsom and St Helier University Hospitals NHS Trust – has one of the largest renal medicine departments in the UK, and relies on Fujifilm SonoSite point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) systems to improve care and patient safety. Dr Pritpal Virdee, a senior registrar in the department, explained: “We have a very busy renal department…
New research indicates that subtle structural features of donated kidneys from living donors may predict the risk of kidney transplant failure in recipients. The findings, which appear in an upcoming issue of JASN, may help clinicians as they evaluate the quality of organs at the time of transplantation. The quality of donated kidneys obtained from living donors is often inferred from their age,…
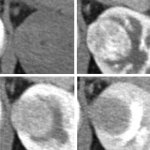
A deep learning method with a convolutional neural network (CNN) can support the evaluation of small solid renal masses in dynamic CT images with acceptable diagnostic performance, according to an article published ahead-of-print in the March issue of the American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR). Between 2012 and 2016, researchers at Japan’s Okayama University studied 1807 image sets from 168…