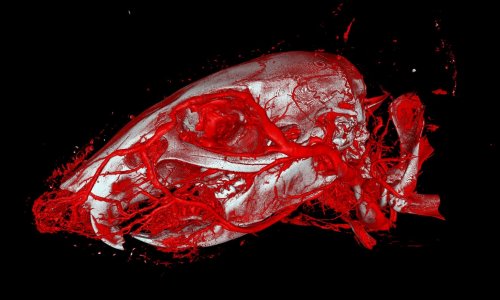
Image source: Kirsten Taphorn / TUM
News • Diagnostic imaging reseach
How contrast agents disperse inside cells
Contrast agents are used very frequently in the difficult task of rendering organ structures visible using conventional X-rays in microCT. The question of the exact concentrations and final locations of these agents within cells has in the past remained largely unexamined, since doing so requires high-resolution methods which are also extremely sensitive.
Now, a research team led by Julia Herzen, Professor of Biomedical Imaging Physics at the Technical University of Munich (TUM), has addressed this question for two previously known exemplary contrast agents. The first, iodine potassium iodide, stains cells unspecifically, which means it does not interact with specific structures. The second contrast agent studied, Eosin Y, contains bromine and dyes the cell cytoplasm, the interior of the cell, since it bonds to protein structures found there.
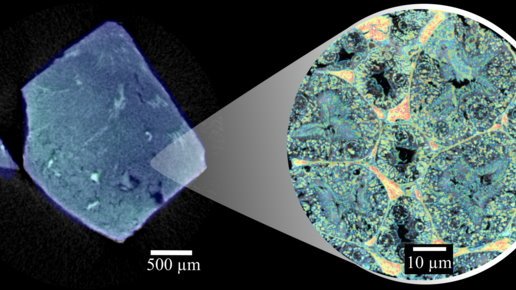
Image source: Paul Scherrer Institute / Mahir Dzambegovic
After dying with the contrast agents, the tissue samples were first analyzed using dual-energy microCT (MicroDECT), a quantitative X-ray imaging method. The researchers used the procedure to determine the overall concentrations of the contrast agents in the tissue. However, this method's resolution is not high enough to represent individual cells.
The next step was to determine how much of the contrast agent had accumulated within the cells and to which individual structures. Here the researchers used a highly sensitive and high-resolution method referred to as ptychographic X-ray computed tomography (PXCT) in a facility at Switzerland's Paul Scherrer Institute. This method is suitable for quantitative analysis and can represent soft tissue as well as organs in greater detail than MicroDECT can.
Using MicroDECT, both contrast agents provided images with comparable levels of contrast. It took ptychography to reveal the significantly different accumulation of the two contrast agents in the cells. “It was surprising to find that for both contrast agents, only very low concentrations were measured in the cells compared to the respective initial solution we used for staining“, says first author Kirsten Taphorn. "In general, we found that Eosin Y accumulated significantly less in the cells than the iodine-based contrast agent."
In the current study the research team investigated two previously known contrast agents. "In the future, ptychography could be used to analyze newly developed contrast agents and to make sure that they actually bond with the desired structures. This would be of particular interest for contrast agents which bond with very specific structures, for example with a certain protein in tumor tissues. This new contrast agent could then be used in combination with virtual X-ray based histology," says Prof. Julia Herzen, head of the study.
Source: Technical University of Munich
02.10.2022