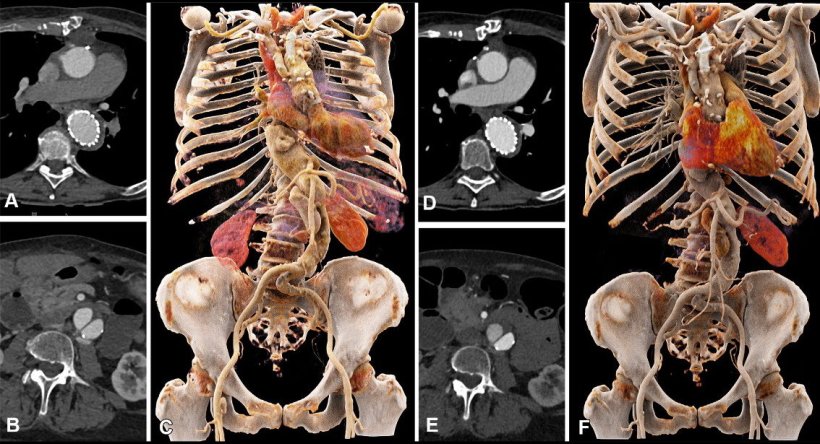
Image source: RSNA; Higashigaito et al., Radiology: Cardiothoracic imaging 2023
News • Angiography advances
Photon-counting CT enables lower contrast media for aortic imaging
Photon-counting detector CT reduces the amount of contrast needed for CT angiography (CTA) while maintaining image quality, according to a new study.
The study is published in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
The portion of the aorta that passes through the chest and abdomen is prone to aneurysms. Risk increases with age. Doctors use CTA with contrast media to examine this region of the artery. While the iodinated contrast media used in these exams is considered very safe, there is a higher risk of adverse reactions in patients with kidney disease, or nephropathy. "Many patients undergoing CTA of the aorta are elderly, and some may suffer from a certain degree of nephropathy," said senior author Hatem Alkadhi, M.D., M.P.H., from the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at University Hospital Zurich in Zurich, Switzerland. "Thus, they might be at risk for a further reduction of their kidney function due to contrast media administration."

Image source: RSNA
Using less contrast media is also good for the environment, as iodine breakdown products have harmful environmental effects. In addition, the supply of contrast media has suffered from shortages due to Covid-19-related disruptions in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Photon-counting detector CT is a new technology that can acquire high-quality images at lower contrast media volume than conventional CT scanners that rely on energy-integrating detectors. It also offers diagnostic quality images at lower radiation dose than those of conventional CT.
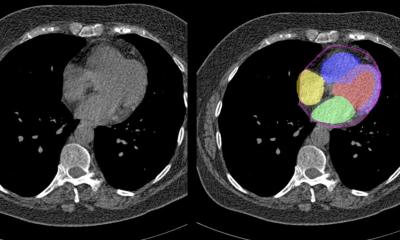
Dr. Alkadhi and his University Hospital colleague Kai Higashigaito, M.D., led a study that looked at a low-volume contrast media protocol with photon-counting detector CT for CTA of the aorta in the chest and abdomen. The study included 100 people, mean age 75. Patients underwent CTA with photon-counting detector CT of the aorta in the chest and abdomen. The patients had received a previous CTA with conventional CT at equal radiation doses. Photon-counting CT had a higher contrast-to-noise ratio, a key measure of image quality, which translates to a low-volume contrast media protocol. Contrast media volume was reduced by 25%.
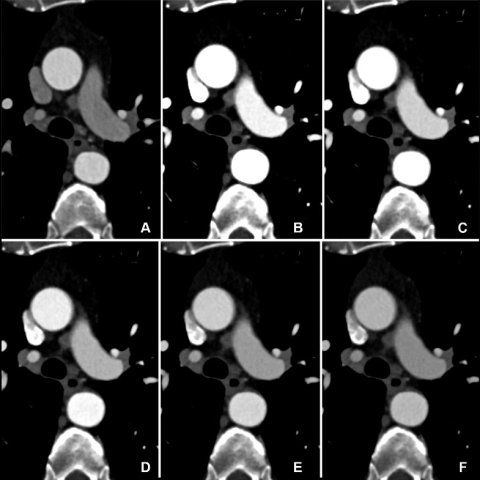
Image source: RSNA; Higashigaito et al., Radiology: Cardiothoracic imaging 2023
Two independent readers rated the image quality of photon-counting CT as higher than that of conventional CT at an equal radiation dose. "We showed that the improved image quality of CTA with photon-counting detector CT systems can be used to reduce the amount of administered contrast media to the patients, without reducing the diagnostic yield of the examination," Dr. Alkadhi said. "Image quality remained at the same level as that of previous CT angiography examinations in the same patients using a conventional CT, despite the fact that we reduced the contrast media volume."
Based on the positive results of the study, Dr. Alkadhi and his colleagues have changed their clinical routine. They now adjust the contrast media protocols in patients undergoing CTA of the aorta in the chest and abdomen.
Besides its superior image quality and spatial resolution, photon-counting CT can provide detailed studies of tissue through its spectral imaging capability. Researchers are looking at this as a way to improve studies of the coronary arteries and the heart muscle. "Based on the initial experience with this new exciting technology, I envision that this detector type will become the standard in CT scanners in the near future," Dr. Alkadhi said.
Source: Radiological Society of North America
27.01.2023