News • Neurodegeneration
New insights on cause of brain calcification
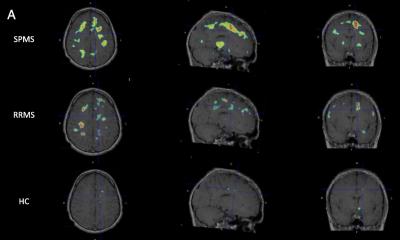
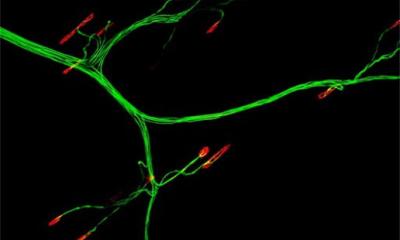
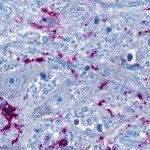
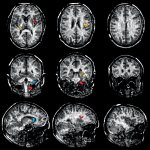
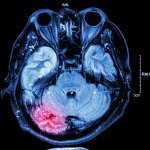
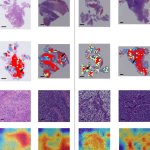
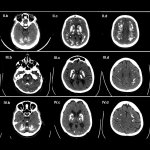
Much like joints or blood vessels, the brain can be affected by calcifications. This can lead to neurodegenerative disease, but is not well studied. Now, researchers from Norway identified a gene that provides new insights.